
What Is RFID sticker and how do they work?
Are you curious about how supermarkets make self-checkout seamless? Or how libraries can quickly scan and inventory thousands of books in a fraction of the time? The answer lies in those unassuming RFID stickers you might have seen on products or books. These small, sticky tags are much more than they appear—they contain embedded RFID chips and antennas that allow for wireless communication with RFID readers. But how exactly do these stickers work, and what makes them so efficient for these industries? In this blog, we’ll break down the science, applications, and benefits of an RFID sticker in a way that’s easy to understand.
The Basics of RFID Sticker
At their core, RFID stickers are small adhesive labels embedded with a microchip and an antenna. “RFID” stands for Radio Frequency Identification, which refers to the technology that allows these stickers to communicate wirelessly with readers. Unlike traditional barcodes, RFID stickers don’t require line-of-sight scanning. Instead, they use radio waves to transmit data, making them faster and more versatile.
The microchip in an RFID sticker stores information, such as a unique identification number or product details. The antenna enables the chip to send and receive signals. When an RFID reader emits radio waves, the sticker’s antenna picks up the signal, powers the chip, and transmits the stored data back to the reader. This process happens in milliseconds, making RFID stickers incredibly efficient for real-time tracking and identification.
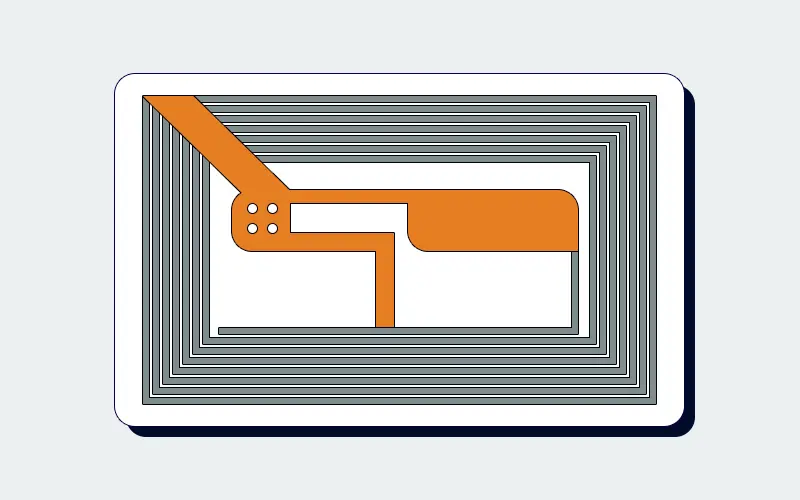
How RFID Sticker Communicate
RFID stickers operate on the principle of electromagnetic coupling. An RFID reader emits a radio frequency signal, creating an electromagnetic field. The sticker’s antenna detects this field and uses it to power the microchip. Once powered, the chip modulates the signal and returns the stored data.
There are two main types of RFID systems: passive and active. Passive RFID stickers rely entirely on the reader’s signal for power, making them cost-effective and ideal for short-range applications like inventory management. Active RFID stickers, on the other hand, have their power source (usually a battery) and can transmit signals over longer distances. This makes them suitable for tracking high-value assets or vehicles.
Three key components that make up a sticker
An RFID sticker consists of three key components: the microchip, the antenna, and the substrate. The microchip is the brain of the sticker, storing and processing data. It can hold a wide range of information, from simple identification numbers to complex product details. The antenna is the communication hub, enabling the sticker to send and receive signals. It’s usually made of conductive materials like copper or aluminum.
The substrate is the material that holds everything together. Depending on the application, it’s often made of paper, plastic, or polyester. For example, RFID stickers in harsh environments might have a durable polyester substrate to withstand moisture and temperature changes. Together, these components create a compact, efficient, and versatile tool for data transmission.

Applications in Everyday Life
RFID stickers are everywhere, even if you don’t always notice them. In retail, they streamline inventory management and enable self-checkout systems. For instance, Zara uses RFID stickers to track clothing items, reducing stock discrepancies by 80%. In healthcare, they help manage medical equipment and patient records, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Logistics companies rely on RFID stickers to track real-time shipments, ensuring timely deliveries. Your passport might even contain an RFID sticker, storing your biometric data for secure identification. These examples highlight the versatility and impact of RFID stickers across industries.
Advantages over Traditional Methods
RFID stickers offer several advantages over traditional identification methods like barcodes. First, they don’t require line-of-sight scanning, meaning you can read multiple stickers simultaneously without precise alignment. This speeds up processes like inventory checks. Second, they can store more data than barcodes, enabling richer information exchange.
Third, RFID stickers are durable and can withstand harsh conditions, making them suitable for outdoor or industrial use. Finally, they enable real-time tracking, providing up-to-the-minute data on items’ location and status. These benefits make RFID stickers superior for modern tracking and identification needs.

Challenges and Limitations
Despite their many advantages, RFID stickers aren’t without challenges. One major limitation is cost. While prices have dropped significantly, RFID stickers are still more expensive than barcodes, especially for large-scale applications. Another issue is interference. Metal and liquids can disrupt radio waves, affecting the performance of RFID stickers.
Privacy concerns also arise, as RFID stickers can be read from a distance without the user’s knowledge. However, advancements in encryption and security protocols address these issues, making RFID technology safer and more reliable.
The Future of RFID Stickers
The future of RFID stickers looks bright, with advancements in technology driving new possibilities. Smaller, more affordable stickers make tagging even low-cost items feasible. Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) enables more innovative, more connected systems. For example, smart refrigerators could use RFID stickers to track food expiration dates and automatically reorder groceries.
Researchers are also exploring biodegradable RFID stickers to reduce environmental impact. As these innovations unfold, RFID stickers will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping a more efficient and connected world.

How RFID sticker change our lives
RFID stickers are changing industries and improving our daily lives by enabling seamless communication, real-time tracking, and efficient data management. As technology evolves, so will RFID stickers’ capabilities. The possibilities are endless, from more innovative supply chains to enhanced personal safety.


